Search
Understanding the Differences Between FPC and FFC Cable
- Sep 20,2023
-
Share
Both FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) and FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) are used to connect connectors at both ends of electronic devices, but they differ significantly in terms of structure, manufacturing processes, and application scenarios. Here's a detailed comparison:
1. Structure and Materials
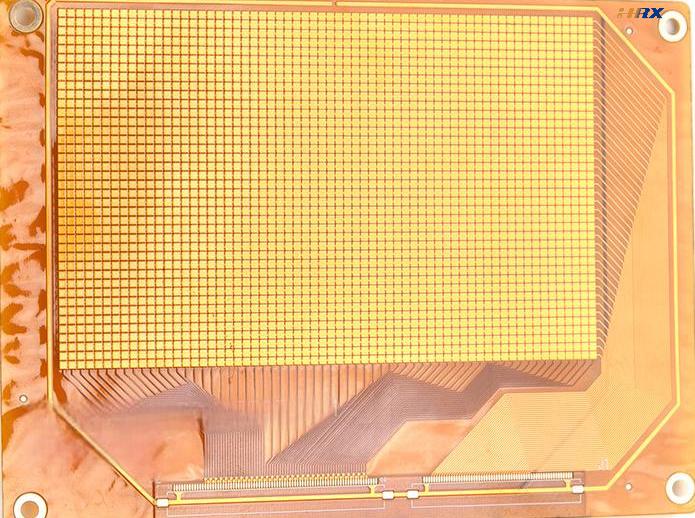
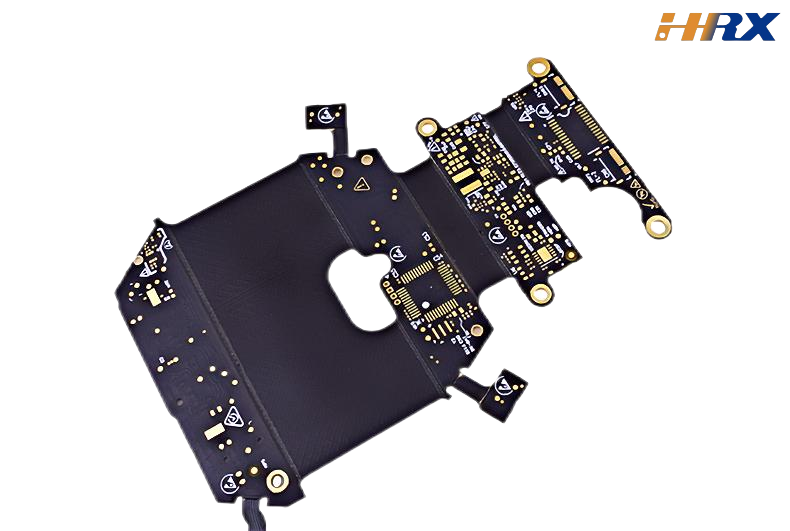
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit):
FPC is composed of multiple layers, including a copper foil conductor layer and Polyimide (PI) as the insulating material.
The circuit on FPC is formed through an etching process, allowing for the design of complex circuits, multilayer connections, and impedance-controlled lines.
FPCs can integrate various electronic components, such as chips and sensors, making them capable of serving as complex functional modules.
FPC also allows for the addition of EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding films to enhance signal integrity and reduce interference.
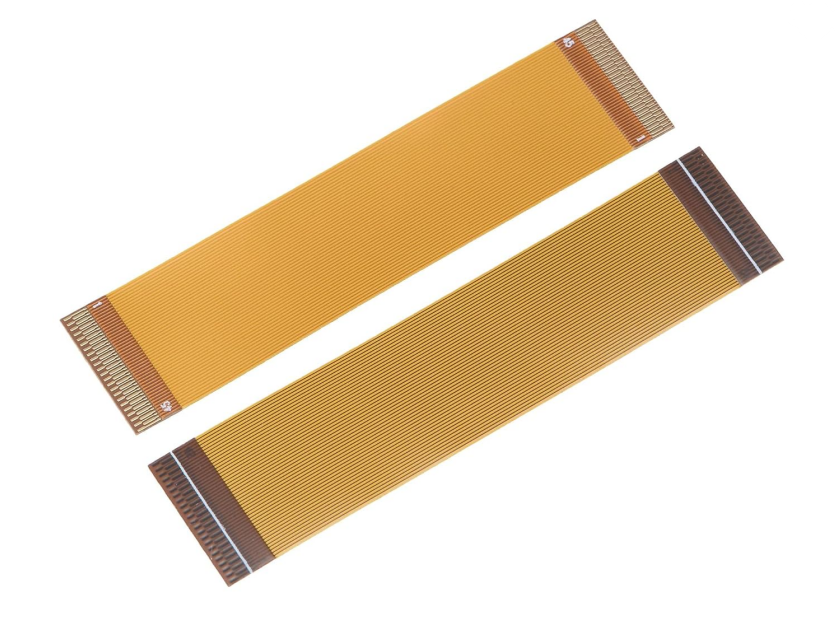
FFC (Flexible Flat Cable):
FFC typically consists of parallel copper conductors laminated between layers of Polyester (PET) or Polyimide (PI) insulation.
FFC generally features a single-layer design with uniform, parallel lines. The design is simpler and often standard, with options primarily focused on selecting different pitch spacing and pin counts.
The surface of FFC can be coated with aluminum foil to provide basic EMI shielding, but the shielding effectiveness is typically less sophisticated than that of FPC.
FFCs are generally rectangular in shape and are manufactured in standard configurations.

2. Manufacturing Process
FPC:
The manufacturing process involves etching the copper foil to create intricate circuit patterns, including multilayer connections and impedance lines. This capability allows for more complex and customized circuit designs.
FPCs can be designed with advanced features such as EMI shielding layers, impedance control, and multi-layer conduction, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
Due to the complexity of the design and the need for precise manufacturing, the production process is more time-consuming and costly compared to FFC.
FFC:
FFC is produced using a simpler lamination process, where parallel copper conductors are arranged in a single layer between insulating materials.
The design is straightforward and standardized, focusing on the selection of pitch spacing and pin numbers rather than complex circuit configurations.
FFC production is faster and more cost-effective, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing of simple, low-cost connectors.
3. Flexibility and Suitability
FPC:
FPCs are highly flexible and durable, capable of maintaining performance even after multiple bends. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high flexibility or complex movement, such as wearable devices and foldable smartphones.
Their ability to support complex circuit designs in limited space makes them ideal for compact, high-density electronic applications.
FFC:
FFCs also offer some flexibility but are better suited for simple, planar connections or slight bends. They are typically used in applications where the cable will remain relatively static, such as internal connections in printers, displays, and home appliances.
Due to their thin and lightweight design, FFCs are well-suited for use in devices with strict weight and space limitations.

4. Application Scenarios
FPC:
FPCs are used in devices requiring high-density circuits, high flexibility, and multilayer connections, such as smartphones, digital cameras, medical devices, and other advanced electronics.
They are also used in applications requiring advanced features like impedance control, EMI shielding, and integrated functionalities, such as camera modules, touchscreens, and display connectors.
FFC:
FFCs are commonly found in simpler applications that require straightforward, point-to-point connections, such as laptops, printers, automotive electronics, and home appliances.
They are particularly useful for connecting components like motherboards, displays, and keyboards, where the design is typically uniform and requires less customization.
5. Cost and Production Efficiency
FPC:
The complexity of FPC design and manufacturing makes it more expensive, suitable for high-end applications that demand intricate circuitry and high performance.
The production cycle is longer, especially for small batches, which adds to the cost but provides superior functionality.
FFC:
FFCs are more cost-effective and efficient to produce, making them ideal for applications requiring simple connections and uniform designs in mid to low-end products.
The simplified manufacturing process allows for rapid, large-scale production, catering to industries where cost and speed are critical factors.
FPC and FFC cables serve similar functions but differ significantly in terms of design complexity, manufacturing processes, and applications. FPCs offer advanced capabilities for complex, high-performance applications, while FFCs provide an economical solution for simpler, standardized connections. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your project, including the need for flexibility, circuit complexity, and cost considerations.

Let’s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!
-
 Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly.
Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly. - WHAT WE DO — PCB Design Solutions — Flex PCB Production — Components Sourcing — FPC&PCB Assembly
- PRODUCTS — Single Sided Flexible Circuits — Double Sided Flexible Circuits — Multilayer Flexible Cirucits — Rigid-Flex Circuits — FPC Assembly — PCB Assembly
- CAPABILITY — FPC Capability — Rigid-Flex Capability — PCB Capability — Assembly Capability
- Copyright © 2024 Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
- Design By BONTOP