Search
Comparative Analysis of Flexible FPC and Rigid PCB: Key Distinctions
- Mar 07,2025
-
Share
In the dynamic realm of electronics, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) form the cornerstone of innumerable devices. Among these, Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCs) and Rigid PCBs stand out as two preeminent types, each boasting distinct characteristics. Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd., a vanguard in the design and production of FPC, PCB, and Rigid - Flex Printed Boards, is here to demystify the disparities between these two pivotal components.
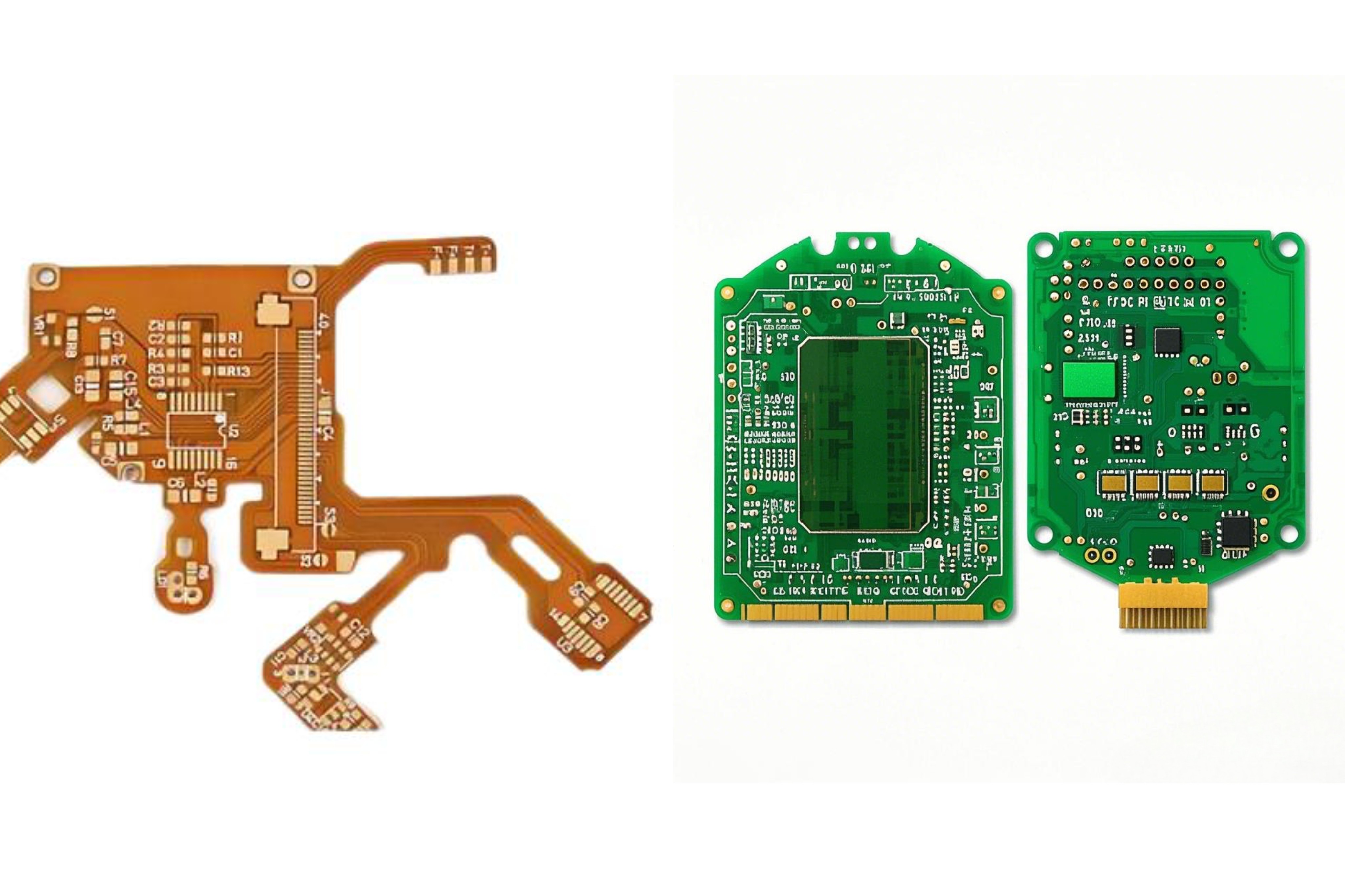
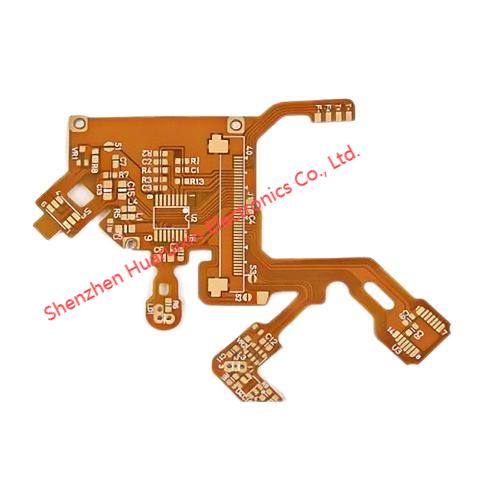
1. Materials
Flexible FPC
Insulating Film: FPCs predominantly utilize materials such as polyimide or polyester film. Polyimide, a paragon in the field of flexible electronics, exhibits remarkable attributes like non - flammability, exceptional geometric stability, and the capacity to withstand soldering temperatures. Its high tensile strength renders it ideal for applications where the board may encounter mechanical stress. Conversely, polyester film, though offering a lower dielectric constant and minimal moisture absorption, has limitations in high - temperature scenarios. In the context of wearable technology, where FPCs are widely deployed, the choice of insulating film becomes crucial for ensuring long - term functionality.
Conductor: Copper foil is the quintessential conductor in FPCs. It can be deposited through electrolytic processes or electroless plating. Electrolytically deposited copper foil features a shiny side and a dull side, with the latter often treated to enhance adhesion to the insulating film. In applications demanding dynamic flexing, such as in the hinges of foldable smartphones, forged copper foil, known for its superior flexibility and smooth, hard surface, takes precedence.
Adhesive: A specialized adhesive, often an anisotropic conductive film (ACF) in advanced FPC applications, is employed to bond the insulating film to the conductive layer. This adhesive not only provides a secure bond but also serves as a protective and insulating cover layer. The quality of the adhesive is of paramount importance, as it must maintain its integrity even when the FPC is subjected to repeated bending and flexing, a common occurrence in flexible display applications.
Rigid PCB
Substrate: Rigid PCBs typically rely on a composite of epoxy resin and fiberglass woven cloth as the substrate. This combination imparts exceptional mechanical strength and rigidity, essential for providing a stable platform for component mounting. The epoxy resin, acting as a binder, holds the fiberglass together while offering robust electrical insulation. In high - performance computing applications, where PCBs need to support powerful processors and multiple components, the choice of substrate material is critical for ensuring reliable operation.
Conductor: Similar to FPCs, copper foil is the go - to conductor in Rigid PCBs. The copper foil is meticulously etched onto the substrate to create the desired circuit patterns. The thickness of the copper foil is tailored according to the current - carrying requirements of the circuit, with thicker foils used for high - current applications such as power supply boards.
Solder Mask Material: A specialized solder mask ink, formulated to meet the stringent demands of PCB manufacturing, is applied to the surface of the Rigid PCB. This mask serves as a safeguard against solder flowing onto unwanted areas during the soldering process, significantly reducing the risk of short circuits and enhancing the overall reliability of the board. In automotive electronics, where PCBs are exposed to harsh environments, the quality of the solder mask material plays a pivotal role in ensuring long - term performance.
2. Structure and Appearance
Flexible FPC
FPCs, true to their name, are highly pliable. They can be bent, folded, and even rolled, enabling innovative and space - efficient designs. This flexibility makes them the preferred choice for applications where the board needs to conform to irregular shapes or accommodate movement within a device. The typical thickness of an FPC hovers around 0.2mm. In regions where components are to be soldered, additional thickening layers, typically 0.2mm or 0.4mm thick, are added to enhance mechanical stability and soldering performance. In the realm of medical devices, such as wearable health monitors, the flexibility of FPCs allows for comfortable and unobtrusive integration.
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs, in contrast, are rigid and flat. They are engineered to provide a stable foundation for component installation. Their inflexible nature ensures that components remain securely in place and electrical connections are maintained. Rigid PCBs come in a range of standard thicknesses, including 0.2mm, 0.4mm, 0.6mm, 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.6mm, and 2.0mm, with the choice of thickness determined by the specific application requirements. In industrial control systems, where PCBs need to withstand vibrations and shocks, a thicker and more robust Rigid PCB is often selected.
3. Manufacturing Process
Flexible FPC
The manufacturing process of FPCs is a complex and intricate affair, demanding specialized equipment and techniques. Precision is of the essence when creating circuit patterns on the flexible substrate to ensure that the circuits can endure repeated bending. Laser drilling, a state - of - the - art technique, is commonly employed to create small - diameter vias, which are vital for connecting different layers of the FPC. The lamination process, too, requires meticulous control to guarantee proper adhesion between the layers without compromising the flexibility of the board. In the production of high - end FPCs for aerospace applications, strict quality control measures are implemented at every stage of the manufacturing process.
Rigid PCB
The manufacturing process of Rigid PCBs, while still requiring precision, is relatively more straightforward. It encompasses steps such as substrate preparation, copper foil etching, drilling, and surface treatment. Standard etching and drilling equipment can be used to create the circuit patterns and holes in the substrate. The process is well - established and highly scalable for mass production. In the consumer electronics industry, where large volumes of Rigid PCBs are required, manufacturers leverage automated manufacturing processes to achieve high productivity and cost - effectiveness.
4. Application Scenarios
Flexible FPC
FPCs find extensive use in applications where space is at a premium and flexibility is a necessity. In the burgeoning field of wearable technology, they are indispensable, conforming to the contours of the body in devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. Foldable smartphones rely on FPCs to enable the folding mechanism while maintaining seamless electrical connections. In automotive interiors, FPCs are used for wiring that needs to navigate around tight corners and irregular spaces. The flexibility of FPCs also makes them suitable for applications in robotics, where they can be used to connect moving parts.
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs are the preferred choice for applications that demand high mechanical stability and reliable electrical connections. They are the backbone of computer motherboards, providing a stable platform for mounting numerous components. In industrial control systems, Rigid PCBs can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference. Power supply boards, which handle high currents and voltages, also rely on Rigid PCBs for their robust construction. In the telecommunications industry, Rigid PCBs are used in base stations and network equipment to ensure reliable signal transmission.
5. Cost and Price
Flexible FPC
Due to the utilization of specialized materials and the complexity of the manufacturing process, FPCs generally command a higher price compared to Rigid PCBs. The cost of high - quality polyimide film and the precision - intensive manufacturing techniques contribute to the elevated price tag. However, in applications where their unique flexibility is non - negotiable, such as in high - end consumer electronics and aerospace applications, the cost is often justifiable. In the development of new flexible display technologies, the initial investment in FPC manufacturing can be substantial but is offset by the potential for increased product functionality and market competitiveness.
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs, with their more straightforward manufacturing process and readily available materials, are generally more cost - effective, especially in large - volume production. Economies of scale come into play, making them an attractive option for applications where cost is a primary consideration. In the mass production of consumer electronics products, such as smartphones and tablets, the use of Rigid PCBs helps keep production costs down without sacrificing performance.
6. Reliability and Durability
Flexible FPC
While FPCs offer unparalleled flexibility, their reliability can be a concern in certain applications. Repeated bending and flexing can induce fatigue in the copper conductors and solder joints, potentially leading to failures over time. However, continuous advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have enabled the development of FPCs that can withstand a significant number of bending cycles. In applications where long - term reliability is crucial, such as in implantable medical devices, rigorous testing and quality control measures are implemented to ensure the durability of FPCs.
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCBs are renowned for their high reliability and durability. Their rigid structure provides robust protection to components and electrical connections, shielding them from mechanical stress. They can better withstand vibrations, shocks, and temperature variations compared to FPCs in many scenarios. This makes them the ideal choice for applications where long - term, trouble - free operation is essential, such as in industrial automation and aerospace systems. In the operation of aircraft avionics, the reliability of Rigid PCBs is critical for ensuring safe and efficient flight.
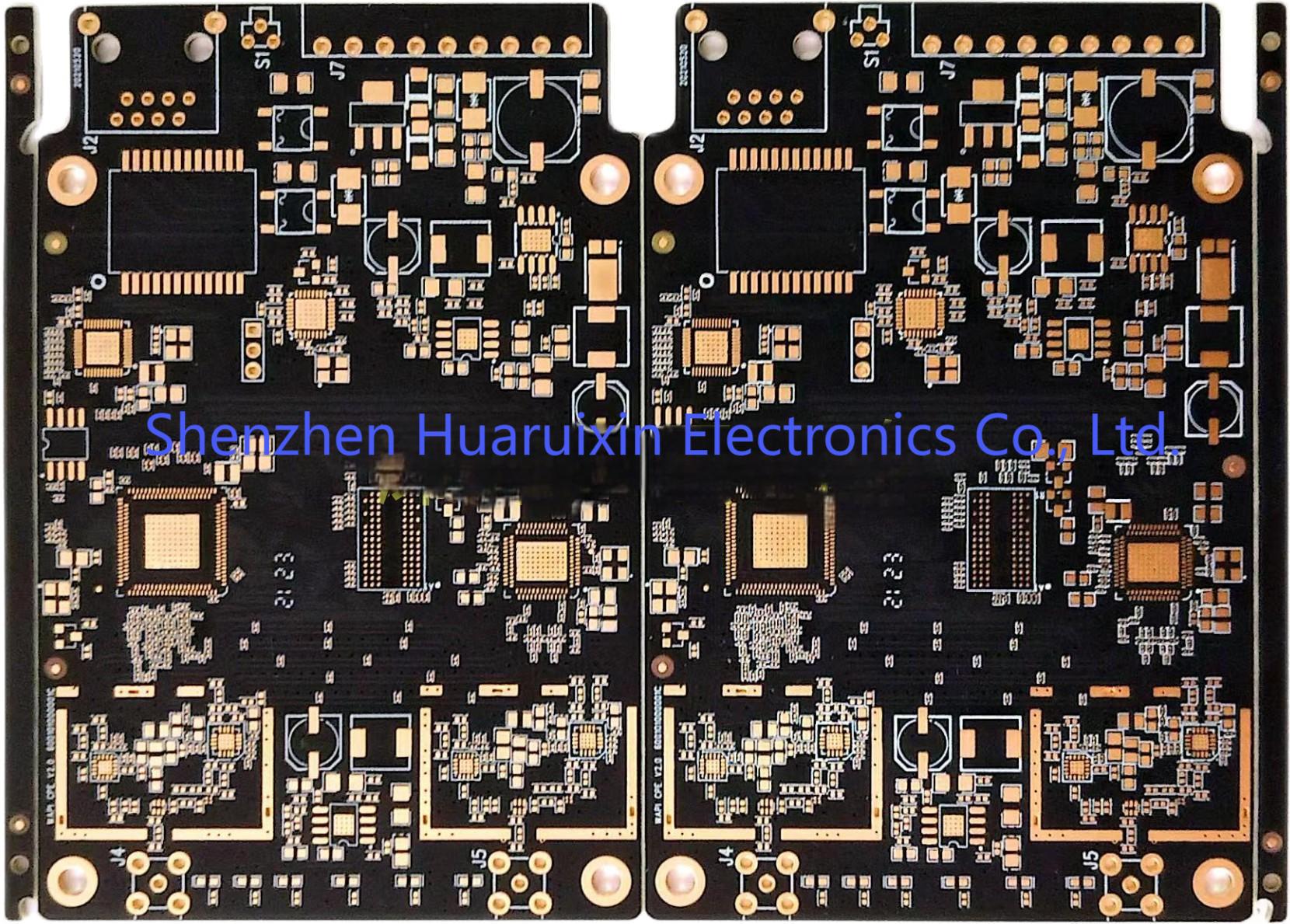
At Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd., our extensive experience in manufacturing both FPCs and Rigid PCBs equips us with profound insights. When choosing between the two, it is imperative to consider the specific requirements of your project. For instance, if your product demands high flexibility and space optimization, an FPC is the optimal choice. Conversely, if stability and cost - effectiveness are your primary concerns, a Rigid PCB may be more suitable. In the manufacturing of FPCs, we place utmost importance on the quality of materials and the precision of the manufacturing process. The selection of top - grade insulating films and copper foils is pivotal for ensuring the long - term performance of the FPC. During the production of Rigid PCBs, we focus on meticulous control of the etching process to guarantee accurate circuit patterns and proper adhesion of the solder mask.
We wholeheartedly welcome new and old friends in the electronics industry to engage in communication and learning. Whether you have queries regarding the differences between FPCs and Rigid PCBs or need guidance on selecting the right type of circuit board for your project, our team of experts is at your service. Let us collaborate to drive innovation in the electronics domain.

Let’s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!
-
 Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly.
Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly. - WHAT WE DO — PCB Design Solutions — Flex PCB Production — Components Sourcing — FPC&PCB Assembly
- PRODUCTS — Single Sided Flexible Circuits — Double Sided Flexible Circuits — Multilayer Flexible Cirucits — Rigid-Flex Circuits — FPC Assembly — PCB Assembly
- CAPABILITY — FPC Capability — Rigid-Flex Capability — PCB Capability — Assembly Capability
- Copyright © 2024 Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
- Design By BONTOP


