Search
5 Principles and Methods for FPC Panelization
- Jul 16,2024
-
Share
In the production of Flexible circuits, panelization is commonly used to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and shorten production cycles, rather than manufacturing individual boards. Several principles need to be followed during the panelization process to ensure smooth production.
1. Maximizing the Use of Space ("Squeeze")
When panelizing, aim to minimize the distance between adjacent boards as much as possible while maintaining manufacturability. This approach reduces the overall panel size, saving production materials and lowering costs.
2. Maintain at Least 2mm Spacing Between Boards
The gap between individual FPC boards should be no less than 2mm. This spacing is crucial for placing alignment holes needed for the production process. In mass production, die-cutting is often used, and alignment holes between each board help ensure precision during die-cutting, preventing misalignment that could lead to defects. For sample production, laser cutting is typically used, and sufficient spacing prevents slight misalignments that could affect the entire panel.
3. Include Etched Markings
Each panel should include etched characters or markings that provide information on panel size, quantity, and other specifications. This ensures accurate verification and matching during the production process.
4. Add Alignment Holes in the Corners
Alignment holes should be placed at the four corners of the panel, with one corner having a distinct marker hole. This ensures consistent orientation in subsequent processes, preventing issues such as incorrect lamination or reversed printing of characters.
5. Fixed Panel Width of 250mm
The panel width should be fixed at 250mm, while the length should also be kept within 250mm when possible. Larger panel sizes can lead to increased deviation and reduced production accuracy, resulting in higher defect rates.
Panelization Methods
With the principles in mind, here are three common methods of FPC panelization:
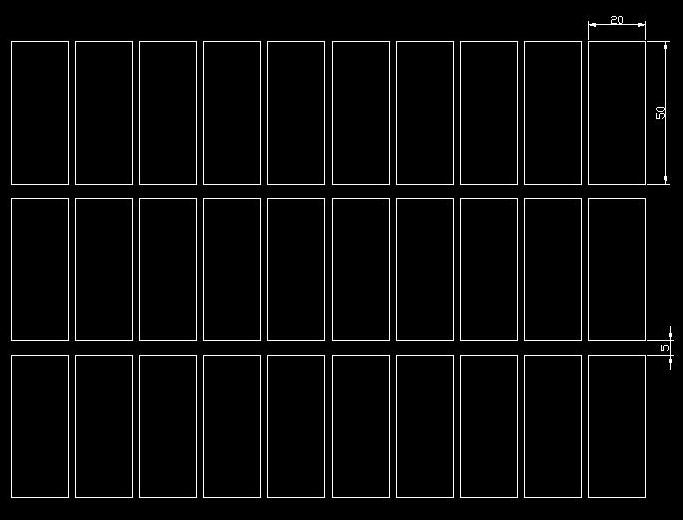
Standard Panelization:
This involves arranging individual FPC boards in a standard array without rotation. It is most suitable for FPCs with regular shapes, such as rectangles, squares, circles, and ovals.
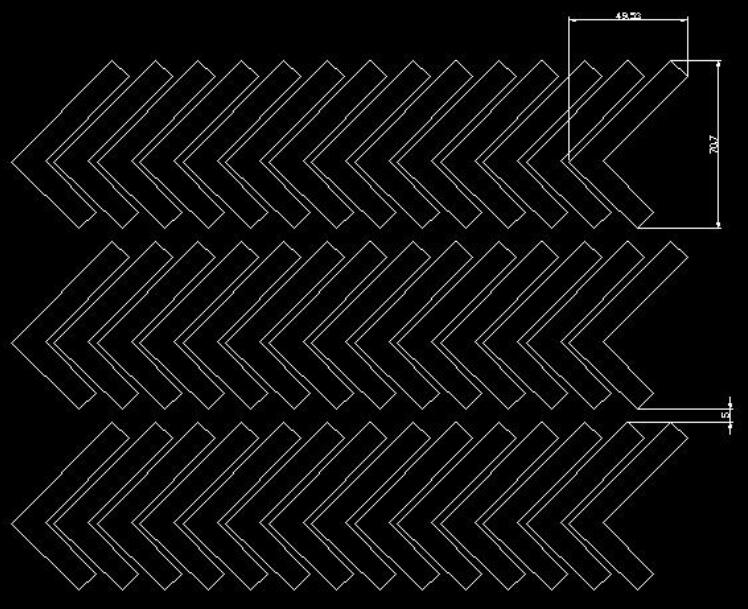
Angled Panelization:
In this method, individual boards are tilted at an angle before being arranged in an array. This technique maximizes the use of space, especially for irregularly shaped FPCs like curved strips or zigzag designs.
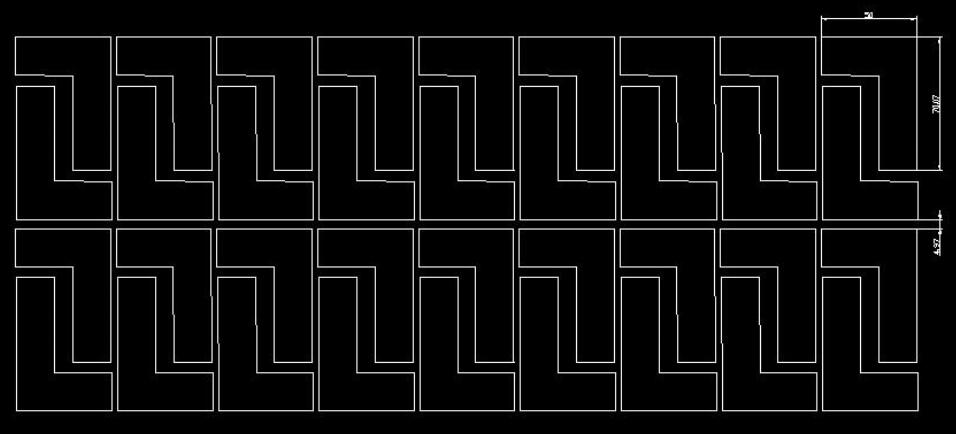
Flip Panelization:
This involves placing one FPC board face up and the adjacent one face down (flipped), arranging them together in a mirrored fashion. This approach helps optimize the use of space on the panel.
Regardless of the method chosen, the primary goal in FPC panelization is always to minimize material usage while maintaining manufacturability. Following these principles will help achieve cost savings and improved production efficiency.

Let’s talk! We’ll provide the perfect solution for you!
-
 Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly.
Huaruixin Electronics mainly produces printed circuit boards as the core business, to provide customers with one-stop solutions for FPC/PCB production, components sourcing and Assembly. - WHAT WE DO — PCB Design Solutions — Flex PCB Production — Components Sourcing — FPC&PCB Assembly
- PRODUCTS — Single Sided Flexible Circuits — Double Sided Flexible Circuits — Multilayer Flexible Cirucits — Rigid-Flex Circuits — FPC Assembly — PCB Assembly
- CAPABILITY — FPC Capability — Rigid-Flex Capability — PCB Capability — Assembly Capability
- Copyright © 2024 Shenzhen Huaruixin Electronics Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
- Design By BONTOP